Sample CAPT Questions - Meteorology
![]()
As a result of studying the Earth’s weather and climate patterns:
Students understand that our atmosphere is dynamic and has patterns of weather systems.
| Explain how winds originate and are affected by the unequal heating of the Earth’s surface, the rotation of the Earth, and the distribution of land and water surfaces. (EIIIA1) |
1. The MAIN source of energy for wind currents on Earth is
a. lightning.
b. heat from the sun.
c. the moon’s gravity.
d. heat from Earth’s interior.
| Explain the water cycle and the energy that drives it. (EIIIA2) |
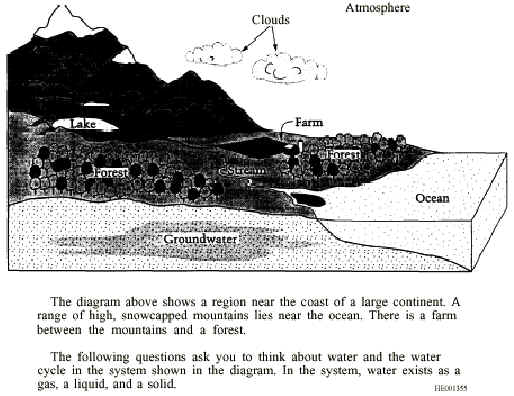
2. Describe how water in the lake can become snow on the mountains in the system shown in the diagram.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
The water cycle is the continuous movement of water between the Earth’s surface and its atmosphere. An illustration of the water cycle is shown below.
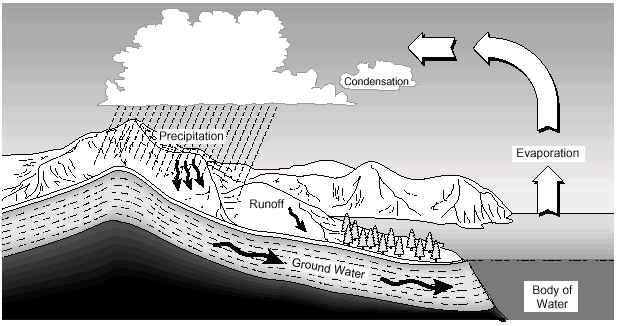
The following processes play important roles in the water cycle:
• evaporation - the changing of a liquid to a gas;
• condensation - the changing of a gas to a liquid; and
• precipitation - the process of depositing water in liquid or solid form.
3. What type of energy drives the water cycle?
a. wind
b. mechanical
c. solar
d. chemical
4. Airline pilots flying high in the sky sometimes report snow falling outside their aircraft, while down on the ground there is no precipitation falling. Which of the following best explains what is happening?
a. The snow condenses to a liquid before it hits the ground.
b. Evaporating water in the air forces the snow back up into the clouds.
c. The snow melts and evaporates before it hits the ground.
d. Water condenses on the snow, forming new clouds.5. In which part of the water cycle are dissolved solid impurities separated from the water?
a. Cloud formation in the atmosphere
b. Precipitation from the clouds
c. Evaporation from the ocean
d. Water flow from the lake to the ocean6. What is the main cause of water evaporation from the ocean?
a. Wind and wave action along the shore
b. Currents in the ocean
c. Heat energy from the ocean floor
d. Heat energy from the Sun7. Explain how clouds can form as air rises. You may draw a diagram as part of your explanation.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
Explain how meteorologists collect and interpret meteorological data from various sources. (EIIIA3) The next two questions refer to the following chart.
| Monday | Tuesday | Wednesday | Thursday | Friday | |
(o F) High Temperature |
43 | 50 | 42 | 53 | 60 |
(o F) Low Temperature |
28 | 38 | 28 | 39 | 45 |
Precpitation |
0.0 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 0.0 | 1.6 |
Average Wind Speed (mph) |
15 | 10 | 7 | 10 | 10 |
8. Based on the weather data in the table, on which day was snowfall most likely to have occurred?
a. Monday
b. Tuesday
c. Wednesday
d. Thursday
9. On which day was the average windchill temperature likely to be the lowest?
a. Monday
b. Tuesday
c. Wednesday
d. Friday
Students understand the reasons for the distribution of climates around the world.
Explain how regional climates are determined by energy transfer from the sun and are influenced by cloud cover, the Earth’s rotation, oceans and mountains. (EIIIB1)
10. In the system shown in the diagram on page 86, the prevailing winds blow from the ocean toward the mountains in September. In June, however, the winds blow mostly from the mountains toward the ocean. In which month, June or September, would the farm get more precipitation? Explain your answer.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
11. Further inland, on the continent, just beyond the mountain range shown in the diagram on page 86, there is a desert that receives very little precipitation. Give an explanation of why this desert receives such a small amount of precipitation.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
Explain the possible causes and effects of global phenomena, including El Niņo, global warming and ozone depletion. (EIIIB2) 12. As a consequence of global warming, coastal areas could:
a. be flooded as ocean levels rise;
b. become further inland as ocean levels recede;
c. get cooler due to more water in the water cycle; or
d. sink as the land becomes less stable from changes in the ocean water;13. One major contributor to global warming is an increased amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. If the number of living plants significantly increased,
a. global warming might get worse because of the increase in carbon dioxide caused by plants;
b. global warming might be reduced because of the decrease in carbon dioxide caused by photosynthesis;
c. global warming might get worse because of the increase in oxygen caused by plants; or
d. there might not be a noticeable impact on global carbon dioxide levels.